Difference between revisions of "Kinds of Developmental Disabilities"
(→Congenital rubella) |
(→Congenital rubella) |
||
| Line 152: | Line 152: | ||
Patent ductus arteriosusPatent ductus arteriosus | Patent ductus arteriosusPatent ductus arteriosus | ||
| + | |||
Pulmonary artery stenosis | Pulmonary artery stenosis | ||
Other heart defects | Other heart defects | ||
| + | |||
Central nervous system: | Central nervous system: | ||
Revision as of 03:22, 5 August 2010
Different types of developmental disabilities
Contents
Nervous system disabilities
These are birth defects that affect the functioning of the brain, spinal cord, and nervous system, which can impact intelligence and learning. These conditions can also cause problems such as behavioral disorders, speech or language difficulties, convulsions, and movement disorders. Some of the common nervous system disabilities include:
Mental retardation
The term mental retardation describes a certain range of scores on an IQ (intelligence quotient) test.The degree of impairment from mental retardation varies widely, from profoundly impaired to mild or borderline retardation Mental retardation can result from a number of different conditions genetic,environmental,infections present during birth,chromosomal abnormalities etc.
Symptoms
Continued infant-like behavior
Decreased learning ability
Failure to meet the markers of intellectual development
Inability to meet educational demands at school
Lack of curiosity
Delays in oral language development
Deficits in memory skills
Difficulty learning social rules
Difficulty with problem solving skills
Delays in the development of adaptive behaviors such as self-help or self-care skills
Lack of social inhibitors
Treatment The primary goal of treatment is to develop the person's potential to the fullest. Special education and training may begin as early as infancy. This includes social skills to help the person function as normally as possible. It is important for a specialist to evaluate the person for other affective disorders and treat those disorders. Behavioral approaches are important for people with mental retardation.
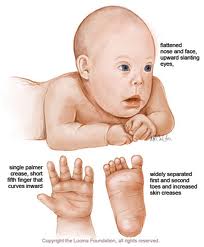
Down syndrome
It is a set of mental and physical characteristics related to having an extra copy of Chromosome 21.There is extra genetic material causes delays in the way a child develops, both mentally and physically.It affects about 1 in every 800 babies.Women age 35 and older have a significantly higher risk of having a child with the condition. At age 30, for example, a woman has about a 1 in 900 chance of conceiving a child with DS. Those odds increase to about 1 in 350 by age 35. By 40 the risk rises to about 1 in 100.
Conditions Associated:
The kids with this disorder tend to grow at a slower rate and remain smaller than their peers. Low muscle tone may contribute to sucking and feeding problems, as well as constipation and other digestive issues. They may have delays in speech and self-care skills like feeding, dressing, and toilet teaching. Down syndrome affects kids' ability to learn in different ways, but most have mild to moderate intellectual impairment. They sometimes face host of medical issues that require extra care. For example, almost half of all children born with DS will have a congenital heart defect. Some have problems with hearing and vision.Other medical complications can be thyroid problems, intestinal abnormalities, seizure disorders, respiratory problems, obesity, an increased susceptibility to infection, and a higher risk of childhood leukemia.
Management:
It is very important to stimulate, encourage, and educate children with Down syndrome from infancy. Programs for young children with special needs are offered in many communities. Early intervention programs, including physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy can be very helpful.Behavioral training can help people with Down syndrome and their families deal with the frustration, anger, and compulsive behavior that often occur. Parents and caregivers should learn to help a person with Down syndrome deal with frustration. At the same time, it is important to encourage independence.Physical therapy may teach movement skills.
Fragile X syndrome
The most common inherited form of mental retardation caused by a defect in a specific part of the Fragile X Mental Retardation -1 gene that causes the body to produce low amounts or none of a certain protein. Without the protein, the brain doesn’t develop normally.
Symptoms:
Intelligence problems, ranging from learning disabilities to severe mental retardation
Social and emotional problems, such as aggression in boys or shyness in girls
Speech and language problems, especially in boys
Treatment: Because a young child's brain is still forming, early intervention gives children the best start possible and the best chance of developing their full potential. Speech and language, behavior, cognitive development, sensory integration, gross motor development, and daily living are areas that often need to be addressed for someone with fragile X syndrome. While many of these areas require physical and behavioral intervention, medication is often an important component of the treatment.
Autism Spectrum Disorders
It is a range of problems that can affect a person's communication skills, social skills, and intelligence. The degree of autism varies from mild to severe.Severely afflicted patients can have a profound intellectual disability. Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASD) can cause severe and pervasive impairment in thinking, feeling, language, and the ability to relate to others. These disorders are usually first diagnosed in early childhood and range from a severe form, called autistic disorder to a much milder form, Asperger syndrome. They also include two rare disorders, Rett syndrome and childhood disintegrative disorder.The cause of autism is unknown.
Symptoms:
All children with ASD demonstrate deficits in 1) social interaction, 2) verbal and nonverbal communication, and 3) repetitive behaviors or interests.They will often have unusual responses to sensory experiences, such as certain sounds or the way objects look.
Possible Indicators of Autism Spectrum Disorders
Does not babble, point, or make meaningful gestures by 1 year of age
Does not speak one word by 16 months
Does not combine two words by 2 years
Does not respond to name
Less language or social skills
Some Other Indicators
Poor eye contact
Doesn't seem to know how to play with toys
Excessively lines up toys or other objects
Is attached to one particular toy or object
Doesn't smile
At times seems to be hearing impaired
Treatment:
While there is no established cure for autism, there are many treatments. Some help manage symptoms, other teach social and behavioral skills, and still others are intended to cure autism altogether.Persons with autism seem to have a higher mortality rate at younger ages due to seizures or infection.
- They need an educational program that is suitable to a student's developmental level of performance.
- Individuals with autism need to be taught how to communicate and interact with others.
- As individuals with autism also seem to be vulnerable to emotional struggles like anxiety, depression and attention problems, the involvement of mental health professionals should be taken.
- Psychotherapeutic approaches that have been found to help improve functioning in some persons with autism include comprehensive behavioral therapy to address problematic behaviors.
- Social skills training and support help people with autism to interact with others.
- Cognitive behavioral treatment too helps in some cases.
- Some medications have been found to help address some symptoms that may present in autism.
Sensory-related problems are often a key part of complex birth defect patterns. For instance:
Children with congenital rubella are likely to be deaf, and to develop cataracts of the eyes.
Children with Williams syndrome have trouble seeing spatial relationships between objects around them.
Those with Fragile X syndrome are often very sensitive to loud noises; they may overreact or have outbursts in reaction to such sounds.
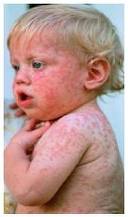
Congenital rubella
Congenital rubella is a group of physical problems that occur in an infant when its mother is infected with the virus that causes German measles.
Risk factors for congenital rubella include:
Not getting the recommended rubella immunization Contact with a person who has rubella (also called the 3-day measles or German measles)
Symptoms in the infant may include:
Cloudy corneas or white appearance to pupil Deafness Developmental delay Excessive sleepiness Irritability Low birth weightLow birth weight Mental retardation Seizures Small head size Skin rash at birth
Complications may involve many parts of the body.
Eyes:
Cataracts Glaucoma Retinitis Heart:
Patent ductus arteriosusPatent ductus arteriosus
Pulmonary artery stenosis Other heart defects
Central nervous system:
Mental retardation Motor retardation Small head from failed brain development Encephalitis Meningitis
Other:
Deafness Low blood platelet count Enlarged liver and spleen Abnormal muscle tone Bone disease
Treatment: There is no specific treatment for congenital rubella. Care involves appropriate treatment of affected systems.Vaccination prior to pregnancy can prevent congenital rubella.
Metabolic Disorders
This group of functional birth defects affects a person's metabolism, which is the way the body builds up, breaks down, and otherwise processes the materials it needs to function. For example, how your body breaks down sugar to create energy is a metabolic process. Two commonly known metabolic disorders include:
Phenylketonuria (PKU)
It is a condition in which a problem with a specific enzyme, a protein that speeds up certain chemical reactions, causes mental retardation.Phenylketonuria (PKU) is a genetic disorder in which the body can't process part of a protein called phenylalanine (Phe). Phe is in almost all foods. If the Phe level gets too high, it can damage the brain and cause severe mental retardation
Symptoms:
About 50% of untreated infants have early symptoms, such as vomiting, irritability, an eczema-like rash, and a mousy odor to the urine. Some may also have subtle signs of nervous system function problems, such as increased muscle tone, and more active muscle tendon reflexes. Later, severe brain problems occur, such as mental retardation and seizures. Other commonly noted features in untreated children include: microcephaly (small head), prominent cheek and upper jaw bones with widely spaced teeth, poor development of tooth enamel, and decreased body growth.
Treatment:
An affected newborn can grow up with normal brain development, but only by managing and controlling phenylalanine (Phe) levels through diet, or a combination of diet and medication. The best treatment for PKU is a diet of low-protein foods. There are special formulas for newborns. For older children and adults, the diet includes many fruits and vegetables. It also includes some low-protein breads, pastas and cereals. Nutritional formulas provide the vitamins and minerals they can't get from their food.
Hypothyroidism
It is a hormonal condition that, if left untreated in an infant, can cause mental retardation.
Degenerative Disorders
Some infants born with degenerative disorders appear normal at birth, but then lose abilities or functions due to the in condition. In these cases, the defect is usually not detected until an older age, when the child or person starts to show signs of loss of function. Some degenerative disorders are the result of metabolic disorders.
Degenerative disorders can cause physical, mental, and sensory problems, depending on the specific defect.Rett syndrome is an example of a degenerative birth defect. This disorder, which usually affects girls, is most often caused by a specific genetic abnormality.