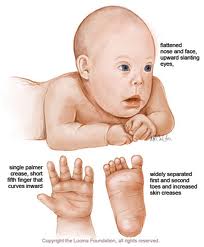
Down syndrome
It is a set of mental and physical characteristics related to having an extra copy of Chromosome 21.There is extra genetic material causes delays in the way a child develops, both mentally and physically.It affects about 1 in every 800 babies.Women age 35 and older have a significantly higher risk of having a child with the condition. At age 30, for example, a woman has about a 1 in 900 chance of conceiving a child with DS. Those odds increase to about 1 in 350 by age 35. By 40 the risk rises to about 1 in 100.
Conditions Associated:
The kids with this disorder tend to grow at a slower rate and remain smaller than their peers. Low muscle tone may contribute to sucking and feeding problems, as well as constipation and other digestive issues. They may have delays in speech and self-care skills like feeding, dressing, and toilet teaching. Down syndrome affects kids' ability to learn in different ways, but most have mild to moderate intellectual impairment. They sometimes face host of medical issues that require extra care. For example, almost half of all children born with DS will have a congenital heart defect. Some have problems with hearing and vision.Other medical complications can be thyroid problems, intestinal abnormalities, seizure disorders, respiratory problems, obesity, an increased susceptibility to infection, and a higher risk of childhood leukemia.
Management:
It is very important to stimulate, encourage, and educate children with Down syndrome from infancy. Programs for young children with special needs are offered in many communities. Early intervention programs, including physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy can be very helpful.Behavioral training can help people with Down syndrome and their families deal with the frustration, anger, and compulsive behavior that often occur. Parents and caregivers should learn to help a person with Down syndrome deal with frustration. At the same time, it is important to encourage independence.Physical therapy may teach movement skills.